
Abstract: with a group of enterprises such as Sina tolist overseasin the form of VIE (variable interest entity), the VIE model has become an important way for the Chinese enterprises to raise funds for listingoverseas.As a corporate system, the innovation of the VIE model is just like that of the financial system, the intellectual property issues of the VIE enterprises are inevitably becoming a concern. Firstly, this article interprets the value appeal and compliance restriction of the VIE enterprises on intellectual property rights, and then discusses the arrangement of assets, risk prevention, consolidation of financial statements and transfer payment of fees in the VIE enterprises.
Key words: VIE,intellectual property rights, patent,strategy
1. Introduction
Since the success of Sina's listing on Nasdaq by using the VIE (variable interest entity) modelin America in 2000, more than 100 companies in the field of TMT (Technology, Media, Telecom), education and training, energy, biomedicine, new energy and other industries have adopted this structural model to list overseas1.At the same time, there are a large number of enterprises using VIE modelfor operation.
There are probably the following reasons for enterprises to adoptthe VIE model:
(1)Facilitating financing.Due to the high domestic listing barriers2 and immature capital markets, it is difficult for the asset-lightcompanies with difficulty of turning a profitat early operation stageto obtain domestic funds3, such as the TMT industry. The adoption of the VIE model can help them get global investment and raise enough capital for development.
(2) Circumventingthe investment restrictions of industrial policies. For the enterprises insome industries in China, foreign investment isrestricted or prohibited. They are severely restricted by a series of regulations, such as the “Provisions of the Ministry of Commerce on M&A of a Domestic Enterprise by Foreign Investors, so it isdifficult for themto get foreign investment and list overseas.
(3) Enhancing corporate visibility. To some extent,
listing overseas can enhance the popularity of the enterprise, increase competitiveness,
andhelp to expandthe international market. With the strong rise of a number of
Chinese enterprises such as Alibaba and Tencent, global financing, operations
and marketing have become the norm. Domestic listing is not the only choice for
local enterprises.
2. The VIE model and its framework
The so-called VIE model refers to the separation of the overseas listing entity from the domestic business operation entity, and the former controls thelatter by means of agreements, rather than equity control in the conventional sense.VIE is an accounting term in the United States. The Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB) issued the No. 46 Interpretation Letter in 2003 in which the concept of VIE was proposed. According to the Letter, if the investment enterprise has the controlling financial interest to an entity which is not obtained by majority voting interest, then such an entity is called VIE.Since this model was firstly used creatively by Sina, it is also known as the "Sina model". This model has been supported by the domestic industry authorities, and has always been a choice for domestic enterprises to get foreign investment and list overseas.
1.1 Building steps of the VIE framework
The basic framework of the VIE model is as follows:
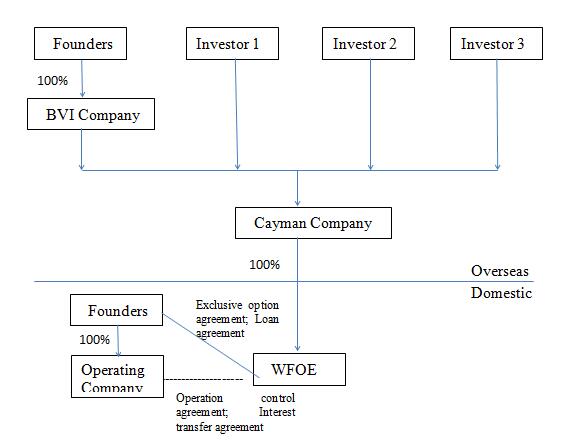
(1) Setting up enterprise in the British Virgin Islands(BVI). The domestic controlling shareholders and investors of the domestic operating companies usually set up the offshore company in the British Virgin Islands for the consideration of legal supervision and tax incentives. The legal system of the enterprisein the above area is easier to be recognized by the international mainstream securities market regulators.
(2) Establishing the enterpriselistedoverseas. Considering the conditions of foreign exchangecontrol and trade restrictions, the main body of the listed enterprise is usually registeredin the Cayman Islands.The enterprise in Cayman Islands hashigher disclosure requirements on ownership structure, directors and executives, which is recognized by the international mainstream stock exchanges.
(3) Establishing the wholly foreign owned enterprise (WFOE).This is mainly based on the consideration of dividend distribution and avoiding the potential conflicts of interest between the Chinese and foreign shareholders. In practice, some enterprises in Cayman Islands set up an enterprisefor special purposein Hong Kong first, and the enterprise in Hong Kong will then set up the WFOE. The main reason for doing so is the optimal tax preferential agreement between Hong Kong and the mainland which allows the enterprise to avoid taxes to the greatest extent and save costs.
(4)
Establishing/reorganizing the domestic operatingenterprise. The domestic
operating enterprise can also adopt the VIE modelafter getting necessary
licenses or permits for businessoperation. Itis mainly responsible for actual
business operation and isthe important source of corporate profits.The VIE enterpriseshave
to concentrate the management and control righton the domestic controlling
shareholders.
1.2 The main agreements of the VIE model
The key to the VIE model is to control the domestic operating enterprise by signing a series of VIE contracts rather than by equity. In practice, the controllingagreementsmainly include the following:
(1) Operational controlling agreements, which mainly include asset operation agreement, shareholder voting agency agreementand authorization agreement. The main purpose is to enable the overseas listed enterprise to indirectly control the decision-making body of the domestic entity. The real effect is that the WFOE controls the operation rights of the VIE enterprise without directly holding the equity.
(2) Profit transfer agreements, which include the service agreements such as management, technical consultation, and project commission, the licensing agreements such as trademarks, patents, and domain names, and the equity pledge agreements.The main purpose is to enable the domestic enterprise to transfer the profits of the VIE enterprise to WFOE in the form of payment of related fees, thus achieving profit transfer.
(3) Exclusive option agreement. It is mainly signed between the Cayman company or WFOE andthe domestic controlling shareholderswith the purpose of reserving channel for purchasing VIE equity.Once the Chinese law allows foreign capital to enter the relevant industries, the overseas enterprisecanget the stock rightthrough acquisition of equity. Itis essentially apledge agreement.
(4) Loan
agreement, which is signed betweenthe WFOE andthe shareholders of the VIE
enterprise.Shareholders can inject corresponding loans into VIE by capital
increase to provide funds foroperation.It is usually an interest free loan for
many years and can be renewed.
3. Analysis of the demand of the VIE enterprise for intellectual property rights
From the beginning of establishment, theVIE enterprisesare inevitably facing global competitionand have a more complex capital structure and higherrequirements for corporate governance.So objectively, they should not only follow the law of market economy, but also standardize their operationaccording to the legal norms of different regions. More importantly, they should be good at using the rules of the mature business environment to find a balance between operational freedom and policy restrictions, so as to reduce non-compliance risks and gain competitive advantages.
The intellectual property demands of the VIE enterprises may include the following aspects:
3.1Demad for listing compliance
In the perspective of IPO, the auditing department pays more attention to intellectual property rights, including patents, trademarks,know-how, franchises, domain names and so on, but forsoftware companies, it will alsoconsider copyright issues.These intellectual property rights are directly related to the public's judgment on the core competitive advantage and sustainable profitability of the proposed listed companies, so they are of great significance to the VIE enterprises.
The capital market mainly concerns the following two aspects ofintellectual property rights:
(1) There should be no risk of significant adverse changes in the acquisition or use of the important assets or technologies, such as trademarks, patents, know-how and franchise rights that are being used by the issuer;
(2) Full disclosure of the intellectual property rights related to theenterprise business and the importance of the asset to the production and operation of the issuer.
Risk prevention mainly includes the following aspects:
(1) Competitors filepatent litigation in order to preventtheenterprise fromgoing public for financing and curb its development;
(2) Some patent "hunters"realisedthe proposed listingcompaniesareeager to pass the initial public offering review to get listed as soon as possible,so theyuse patent infringement litigation to force them to pay more licensing fees for settlement.
Therefore, enterprises should consider all the aspects comprehensively and avoid lawsuit disputes. Of course, the most important is to pay attention to the intellectual property stockand risk warning ofintellectual property related to the core business.
3.2 Demand for protocol control
Under the VIE model, the overseas listedentitycontrols the domestic operating entity through VIE agreements, instead of equity in the traditional sense.It is not easy forthe two partiesto unilaterally dispose of a sophisticated protocol control structure. In addition, the investors and domestic controlling shareholders have the same interests, so that they usually do not easily default.But this does not mean that there is no risk for such a controlling model.
The VIE control agreement is essentially a free contract signed under the autonomy of the two parties, the greatest risk is the invalidity of the contract, as it can easily become invalid or revoked or breached unilaterally due topolicy supervision, the moral level of the controlling shareholders, and other unknown factors. Although the WFOE may replace the domestic controlling shareholder in exercising its shareholder rights in the domestic enterprise under the equity principal-agent contract, the domestic controlling shareholder can unilaterally terminate the contract at any time in the name of the stakeholder of the domestic enterprise. Even if the controlling shareholder has taken responsibilities for the breach of contract, the investor may still lose control of the VIE enterprise.This is also the biggest defect of the VIE protocol control model comparedwith the equity control mode, and thishas been verified by the VIE affairof Alipay.
Therefore, in order to control the enterprise, it has become a natural motivation for the investors to put more intangible assets especially intellectual property rights under the control of the WFOE. It is particularly important for the enterprises in the TMT industry. Under such business model, perhaps the most important thing for the enterprise is not necessarily the fixed assets, such as machinery, factories and land, but the intangible assets solidified in intellectual property rights. In practice, the large number of service agreementssigned between WFOE and the VIE enterprise makes the motivation come true, such as the agreements on management, technical consultation and project commissioning.
According to the stipulation of the technical contract in Chapter 18 of the Contract Law of China4, the trustor and the contractor can agree on the ownership of the achievements of invention.Therefore, it is absolutely possible to specify thatthe rights associated with inventionbelong to the trustorin VIE agreement, so that the intellectual property rights produced by the VIE enterprise can be transferred to WFOE.
3.3 Demand for transfer pricing
The enterprisesadopting the VIE model have relatively complicated internal structure and a large number of connected transactions. To reduce transaction costs through connected transactions is a common practice for modern enterprises, which is also an important means for the VIE enterprise to implement business strategy. Usually, the profits of the VIE enterprises are transferred to WFOE in the name of service fee or licensing fee, and then transferred to the overseas listed entities.
The highly volatile licensing fee or service feeallowsthe enterprises within the VIE framework to manipulatecosts and profits, which may lead to certain tax risks.At present, the transfer pricing regulations in China require enterprises to reasonably explain the pricing of intangible assets inthe simultaneous data and advance pricing agreement5.In practice, to conduct tax planning through the transfer pricing of intangible assets is a common practice, which is generally carried out from two perspectives:
(1) Transfer profits to the affiliated enterprises with low or exempted tax rates by taking advantage of the lowincome tax rates,loose tax reduction policiesand other preferential policiesand of the region where the enterprise belong;
(2) Transfer the profits of the profitable enterprises to the unprofitable enterprises to minimize the tax burden on the whole structural level.
Therefore, from the perspective of the distribution of intellectual property rights, the VIE enterprises need to consider appropriate intellectual property mapin the corresponding operating enterprises to help themgetthe tax preferential qualifications.For example, the Enterprise Income Tax Law of China stipulates that 15% of the corporate income tax is exempted for the hi-tech enterprises. 6The enterprises with both software enterprise certification and software product registration, from the first profit-making year, can enjoy the preferential tax policy of 2 years of exemption and 3 years of reduction by half,5 years of exemption and 5 years of reduction by half and paying tax at the rate of 10%.7
The core issue of the transfer pricing of intellectual property rights is how to fix the price, because the connected transaction of intangible assets under the VIE model mainly involves trademarks, patents, domain names, licensing of know-how, etc., and the factors affecting the pricing are more complex. Firstly, intellectual property rights have the characteristics of unityand exclusiveness, and there is nouniform market price to refer to. Pricing and valuation have great fluctuations and differences and are difficult to measure accurately.Secondly, intellectual property rights are only traded among the affiliated enterprises and only for a single entity. It is difficult to select a comparable reference from the outsideat a time.
Therefore, the VIE enterprises need to be particularly cautious when making transfer pricing of intellectual property rights, in order to avoid or reduce tax risks.
1.4 Demand for actual business operation
The investors have an incentive to separate the ownership of intellectual property rights from the actual operation of the VIE enterprises, and in practice, a license may be granted to the VIE enterprises for use. However, there are also special demands for the ownership of intellectual property rights in the actual business operation of the enterprises. Enterprises should arrange in advancethe intellectual property rights among the main entities.
Taking the demand for trademarks in the mobile phone business of TMT industry as an example, if the enterprisesdetermineto engage in mobile phone production, research and development, and sales, they have to pay attention to the special requirements in practice on theproduction, network access, sales and other aspects.
First of all, if theenterprise plans toengage in mobile phoneproduction,thenitsregistered business scope must include mobile phoneresearch and development and production,and the change of business scope requires a series of pre-approval conditions.For example, the policy of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on the qualification of mobile phone production enterprisesstipulates that first, the registered capital of the enterpriseshould be more than or equal to 20 million RMB; second, the registered business scope shouldinclude“R&D, production and sales of cell phones or mobile phones”; third, the enterprise must have ISO9000 certification; fourth, the enterprise must have a trademark; fifth, the address of the ISO certification and that of business license must be the same; sixth, the nameof the enterprise in the business licenseandthe name of the enterprise which is protected bytrademarkmust be the same.
Secondly, the enterprise marketing is multi-level, and in addition to the traditional offline market, the Internet online market is becoming more and more important. If the enterprise wants to open online stores in the online malls such as TMallor JD.com, ithas to meet their requirements. For example, TMall requires not only routine business licenses but also certificate of legal use of trademarksfor entrance. Forown trademark, a trademark registration certificate or notice of acceptance of theapplication for trademark registration issued by the Trademark Office of the State Administration for Industry & Commerce should be provided; for trademark licensing, the certificate of exclusive licenseshould be provided. 8The average time to receive the notice of acceptance of trademark application issued by the Trademark Office of the State Administration for Industry & Commerce is 4 months, and the average time to get the trademark grantedis 9 months.
Therefore,
enterprises shouldprepare for trademark application or licensingin an earlier time
in order to ensure normal operation.
4. Suggestions on the intellectual property strategy of theVIE enterprises
As an important part of enterprise management,intellectual property strategyshould play a very important role in the management strategy of the enterprise. Therefore, enterprises should fully consider the requirements of intellectual property management and the governance structure of the VIE model when developingthe intellectual property strategy.In view of this andconsidering the actual operating situation of the VIE enterprises, this article puts forward the idea of "trinity" for the development of intellectual property strategy.
(1) Supportability: the intellectual property strategy of the VIE enterprises should be subordinate to the overall requirements of the VIE agreement, serve the overall business development strategy of the enterprise, ensure the business safety, and enhance the core competitiveness.
(2) Balance: the intellectual property strategy of the VIE enterprises should focus on balancing the interests of the domestic controlling shareholders and investors, coordinate various forces and maximize the value of intellectual property assets.
(3) Foresight: the intellectual property strategyof the VIE enterprises should focus on the future development trend of the enterprises and overall consideration in time and space in advance, so as to avoid the risks that enterprises may encounter in the course of operation and listing.
Under the guidance of the ideology of“trinity”, this article puts forward the following suggestions on the intellectual property strategy development of the VIE enterprises from three aspects: the layout strategy of intellectual property, risk prevention and operation strategy.
4.1 Intellectual property layout strategy
There is no fixed and unified pattern for intellectual property layout. Enterprises shoulddevelop theintellectual property layout strategy according to the dynamics ofmarket competition, resources, and investor relations.Generally, three forms of intellectual property right arrangementcan be summarized, the advantages and disadvantages of the three forms are analyzed in the following table:
|
IP owner |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
VIE enterprise |
1. Meet the requirements of business operation and enhance the competitiveness of the VIE enterprise; 2.The domestic enterprise can enjoy local government subsidy. |
1.Investor’s control is the weakest; 2. Not conducive to the implementation of profit transfer agreements. |
|
WFOE |
1. Investor’s control is strong; 2. Can enjoy the domestic IP grants; 3. Easier to implement profit transfer agreements. |
1. Reduce the competitiveness of the VIE business IP. |
|
Cayman company |
1. Investor’s control is the strongest; 2.Increase the proportion of intangible assets of the listed entity. |
1.Overseas enterprise generally cannot enjoy the domestic IP subsidy |
In practice, all the above three forms of intellectual property assetarrangementhave been adopted by enterprises, and each plays an important role in the development of the enterprises. Enterprises can rationally allocatethe assets according to their own conditions, taking into consideration of the above-mentioned factors and other factors such as government projects and application for national high-tech certificate, in order to meet the main business needs.
In addition, the VIE enterprises are generally young and developingrapidly, and the intellectual property layout often lags behind the market development. One of the important reasons is that employees do not want to or cannot do intellectual property management. Intellectual property rights, as a result of intellectual activities, have a unique nature. Only by establishing a good incentive mechanism can the intellectual achievements of enterprises be produced continuously.The incentive mechanism for employee invention in enterprises usually includes both material and spiritual incentives. All staff should be encouraged to take an active part in the cultivation of the intellectual property advantages of enterprises.
The core of the incentive mechanism is that enterprises should build a healthy value exchange system, so that employees will do, want to do intellectual property management.The reward conditions should be designed reasonably, neither too high to let employees feel unattainable, nor too low to achieve the purpose ofpromoting technological progress; at the same time, enterprises should consider the timeliness and long-term issues. Untimely incentiveshave no effect, and too early incentivecan reduceemployees’ long-term invention motivations.
The enterprise the author works for has some experience in this respect. CloudMinds is a VIE company established in 2015. Since its inception, the company has created aninvention incentive system called the Patent Partnership Plan (PPP), which aims primarily at giving full play to the enthusiasm and creativity of employees, quickly accumulating and protecting intangible assets, promoting the play of the value of intangible assets, improving the quality of patents and work efficiency. The core contents of the system include employeeinvention award, high-quality patents award, and patent implementation award. Since the implementation of the system, more than 300 patents have been applied.
4.2Intellectual property risk prevention
Many scholars have discussed theprevention of intellectual property risk of enterprisesin the conventional sense. This article focuses on preventing the intellectual property risk related to employee turnover. At present, the VIE enterprises are mostly concentrated in the TMT industry, and the general characteristics are that they have just been established with a high turnover rate and proportion of talents. According to the Two-Eight Principle of Management, 80% of the company's performance is contributed by 20% of the staff. This 20% is the core staffand are essential and indispensable to the enterprise. The core staff's leaving is obviously harmful to the enterprise.
Three aspects should be considered in the intellectual property management related toemployees: 1. labor contract management; 2. trade secret management; 3. intellectual property management.
The Standards for Enterprise Intellectual Property Management promulgated in 2013 was drafted and issued by the National Intellectual Property Administration and is the first national standard for enterprise intellectual property management in China. The Chapter 6.1 Human Resources Management9 has fully elaborated the management strategies that enterprises should pay attention to from the perspective of intellectual property rights. The VIE enterprises can refer toand embed it into the corresponding management links.
4.3 Intellectual property operation strategy
The ultimate goal of intellectual property strategy is to create profits by relying on intellectual property rights.Especially for the VIE enterprises, great investment and efforts are needed in the process of innovation and privilegization. When the technological achievements are finally under authorized protection, the enterprises must consider how to rely on them to create higher value, so as to make up for the investmentin early research and development, and even create more profits.On the other hand, according to the VIE agreements, the profits of the VIE enterprises should be transferred toWFOE in the name of intellectual property licensing fees, and then to the overseas listed entities.
Therefore, the VIE enterprises need to consider the following two points in intellectual property operation:
(1) Internal operation
The internal operation of the VIE group companies can include the following models: intellectual property licensing, intellectual property transfer,buying a share withintellectual property rights, and intellectual property pledge financing. These models are usingthe exchange value of intellectual property rights.Enterprises should adopt the suitable model according to the specific circumstances, business strategies and opportunities.
(2) External operation
The feasibility strategies for external operations include:
Impeding supply: the strategy of impeding supply is essentially to obstruct the supply of competitors through the advantages of intellectual property rights, thus influencing the industrial development, gaining competitive advantages and reflecting the value of R&D.
Product/business promotion: it refers tousing the intellectual property rights of enterprisesto accelerate the promotion of products and business so as to achieve the overall strategic purpose of the enterprise.
Cost reduction: the main purpose of this kind of intellectual property application strategy is to use the intellectual property to reduce the procurement costs of the enterprise.
Direct
licensing: under this model, the enterprises directly license to the outside
world. It is a more traditional strategy.
5. Several other issues that the VIE enterprises need to pay attention to in terms of intellectual property rights
The VIE enterprises also need to consider other problems, and this article temporarily proposesthemas open questions.
5.1 Financial treatment of intellectual property rights
The VIE enterprises shouldconsider more aspectscompared with ordinary enterprises because they have to consider the requirements of the corporate and financial systems in China, the United States and even Hong Kong at the same time.
For example: how to define and calculate the intellectual property rights in accounting and how to include it into the costs or expenses?How to conduct intellectual property accounting to help the executives and investors to accurately and timely understand the company's operating status for better planning and decision-making in the next stage?
5.2Cost control of intellectual property rights
Cost cannot be avoided in intellectual property layout and the high-quality intellectual property layout is usually accompanied by cost consumption.
Have the cost structure and characteristics of intellectual property rights been effectively analyzed?How to effectively reduce the cost of intellectual property layout?Does the intellectual property management ofthe enterprises consider introducing the ideology of strategic cost?How to achieve rational R&D, restraint in layout, being well-maintained, profitable operation, and win-win situationin the intellectual property inputs?
5.3 Globalization strategy of intellectual property rights
The intellectual property rights of the VIE companies need to be globalized. It's hard to imagine that a company going to list on Nasdaq has no patents in the United States.Then, how to effectively acquire internal resources to carry out overseas patent layout?How to effectively acquire overseas patent assets that can enhance the competitiveness ofthe enterprise?How to control the factors such as time, space, pace,and cost while considering the global layout of intellectual property rights?
In summary, the VIE model is adopted by more and more export-oriented enterprises, and will continue to be usedfor some time before the regulatory policy changes.Enterprises should fully understand the control requirements of the VIE agreements,develop a rational intellectual property strategy,andfully play its rolein the VIE enterprises. This is a new challenge to the operators and intellectual property decision makers in the enterprise.
Remarks:
1. This data is cited from the Research on the Tax Lawfor Overseas Indirect Listing of the VIE Framework, Hao Lijun, Li Gang.
2. According to the Notice on Issues Related to Enterprises’ Application for Overseas Listing issued by China Securities Regulatory Commission in 1999, the conditions for enterprises to apply for overseas listing are: (1) comply with the relevant laws, regulations and rules on overseas listing in China. (2) The purpose of raising funds should conform to the national industrial policy, the foreign capital utilization policy and the national regulations on the establishment of fixed assets investment projects. (3) The net assets are not less than 400 million RMB, the after-tax profits are not less than 60 million RMB in the past year with growth potential; according to a reasonable expected P/E ratio, the amount raised is not less than 50 million US Dollars. (4) Have a standardized corporate governance structure and a better internal management system, and a stable senior management rank and a higher management level.(5) After listing, there is a reliable source of foreign exchangefor the dividend payout, and is in conformity with the relevant national provisions onforeign exchange control. (6) Other conditions stipulated by China Securities Regulatory Commission.
3. According to the Interim Management Measures for the Initial Public Offerings and listing on GEM issued byChina Securities Regulatory Commission in 2009, the main criteria for listing onGEM are: publisher’s application for initial public offerings should meet the following requirements: (1) the publisher is a limited cooperation established in accordance with the law and has been operating for more than three consecutiveyears. If the limited cooperation is converted into the joint stock limited company as a whole according to the original book value of net assets, the duration of its operation can be calculated from the date of the establishment of the limited cooperation; (2) the continuous profits in recent two years and the accumulated net profits in the last two years are not less than 10 million RMB; or the continuous profits in the past one year and the operating income in the last year is not less than 50 million RMB. The net profit is calculated on the basis of deducting non-recurring gains and losses; (3)the net assets at the end of the latest period are not less than 20millionRMB and there is no uncompensated deficit; (4) the total share capital after issuance is not less than 30 million RMB. Article 12:the registered capital of the publisher has been paid in full, and the formalities for transferring the property rights of the assets used as capital contribution by the initiator or shareholder have been completed. There are no significant ownership disputes over the principal assets of the publisher.
4. Article 339 of the Contract Law:for the inventions of commissioned development, unless otherwise agreed by the parties, the patent application right belongs to the developer.If the researcher/developer obtains the patent right, the client can implement the patent free of charge.In the case that thedeveloperintends to transfer the patent application right, the client should have the priority to obtain itunder the same conditions.
Article 340:for the inventions of cooperative development, except as otherwise agreed by the parties, the patent application rightbelongs to the cooperative parties.Where one party intends to transferthe joint patent application right, the other party should enjoy the priority of obtainingit under the same conditions.
Article 341:for the technological secret achievements completed throughentrusted development or cooperative development, the parties concerned should agree on the right to use, transfer, and benefit distribution. If there is no agreement or the agreement is unclear, or it cannot be settled according to the provisions of Article 61 of this Law, all the parties concerned have the right to use or transfer,but the entrusteddevelopershould not transfer the research and development results to a third party before delivering them to the client.
5. In 2009, the State Administration of Taxation published a notice on the issue of the Measures for the Implementation of Special Tax Adjustment (trial):
Article 10: related transactions mainly include the following types: (2)transfer and use of intangible assets, including land use rights, copyright, patents, trademarks, customer lists, marketing channels, brands, trade secrets and other proprietary technologies, and the provision of ownership transfer and use of the industrial property rights, such as industrial designs or utility models.
Among them, Articles 11 and 14 also stipulate in detail.
6. Article 28 of the Enterprise Income Tax Law.
7. Stipulation of the Notice on Further Encouraging the Software Industry and IC Industry to Develop Enterprise Income Tax Policy
(1) For theIC manufacturers,if the width of the IC lineis less than 0.8 microns (including), after confirmation, they will enjoy the exemption of enterprise income tax for the first and second year since the profit-making year before December 31, 2017. They will enjoy the reduction of enterprise income tax by half of the statutory tax rate of 25% from the third to the fifth year, and enjoy it until the expiration of the term.
(2) For the IC manufacturers, if the width of the IC linesis less than 0.25 microns or the investments exceed 8 billion RMB, theycan pay the enterprise income tax at a reduced rate of 15% after verification. The companies with the operating period over 15 years can enjoy the exemption of enterprise income taxin the 1st-5th year from the profit-making year before December 31, 2017; and they can enjoy the reduction of enterprise income tax by half of the legally levied rate of 25% from the sixth to the tenth year, and will enjoyit until the expiration of the term.
(3) The newly established IC design enterprises and qualified software enterprises in China will, upon confirmation, enjoy the exemption of enterprise income tax in the first and second year since the profit-making year before December 31, 2017; and will enjoy the reduction of enterprise income tax by half of the statutory tax rate of 25% from the third to the fifth year, and enjoy it until the expiration of the term.
(4) For the key software enterprises and IC design enterprises included in the National Planning and layout, if they did not enjoy the tax-free preferential treatment in the current year, they can pay the enterprise income tax at a reduced rate of 10%.
8. See the list of brand qualifications atthe following website:https://pages.tmall.com/wow/seller/act/investment-promotion?spm=a223k.8006297.6107009570.6.18a5d8e4LzVKmd&acm=lb-zebra-14053-462070.1003.4.557679&scm=1003.4.lb-zebra-14053-462070.OTHER_14472763668712_557679#7:14.
9. Enterprise Intellectual Property Management Regulations:
6.1.4 Education and training: organizing theeducational trainings on intellectual property, including the following contents:
(a) Stipulate the requirements for the educational trainingsfor the intellectual property staff, and develop plans and implement them.
(b) Organize the intellectual property trainings for all employees in accordance with their business areas and job requirements, and make records.
(c) Organize intellectual property trainings for the senior managers, and make records.
(d) Organize trainings on intellectual property rights for the R&D staff and other personnel closely related to intellectual property, and make records.
6.1.4 Entry for new recruits
Proper intellectual property background checks should be conducted among new employees to avoid infringement of other people's intellectual property rights. For the positions closely related to intellectual property rights, such as research and development, new employees should be required to sign the intellectual property declaration documents.
6.1.5 Quit
Enterprises should remind the employees quitting their jobsof the intellectual property rights; when the employees involved in the core intellectual property rights quit their jobs, they should sign the intellectual property rights agreement or competition restriction agreement.
